A well-determined structure is at the basis of mineral formation. Atoms unite together and create crystals with smooth faces and whose shape has precise geometric characteristics. In nature, crystals do not always appear in their regular form.
Scientists, in the interest of organization, have created their own very geometric classification for gemstones and minerals.
Crystallographic classification
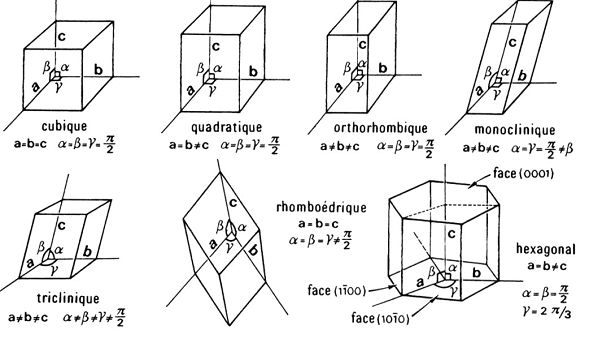
The classification of forms is organized according to 7 systems:
- The cubic system: such as for example Diamond
- The tetragonal system: such as for example Zircon
- The hexagonal system: such as for example Emerald (Beryl)
- The rhombohedral system: such as for example Sapphire (Corundum)
- The orthorhombic system: such as for example Topaz
- The monoclinic system: such as for example Malachite
- The triclinic system: such as for example Labradorite
Key takeaways
This classification allows gemologists to better understand the internal structure of gemstones and identify their optical and physical properties. Each crystal system has unique geometric characteristics that influence the appearance and behavior of the precious stone.